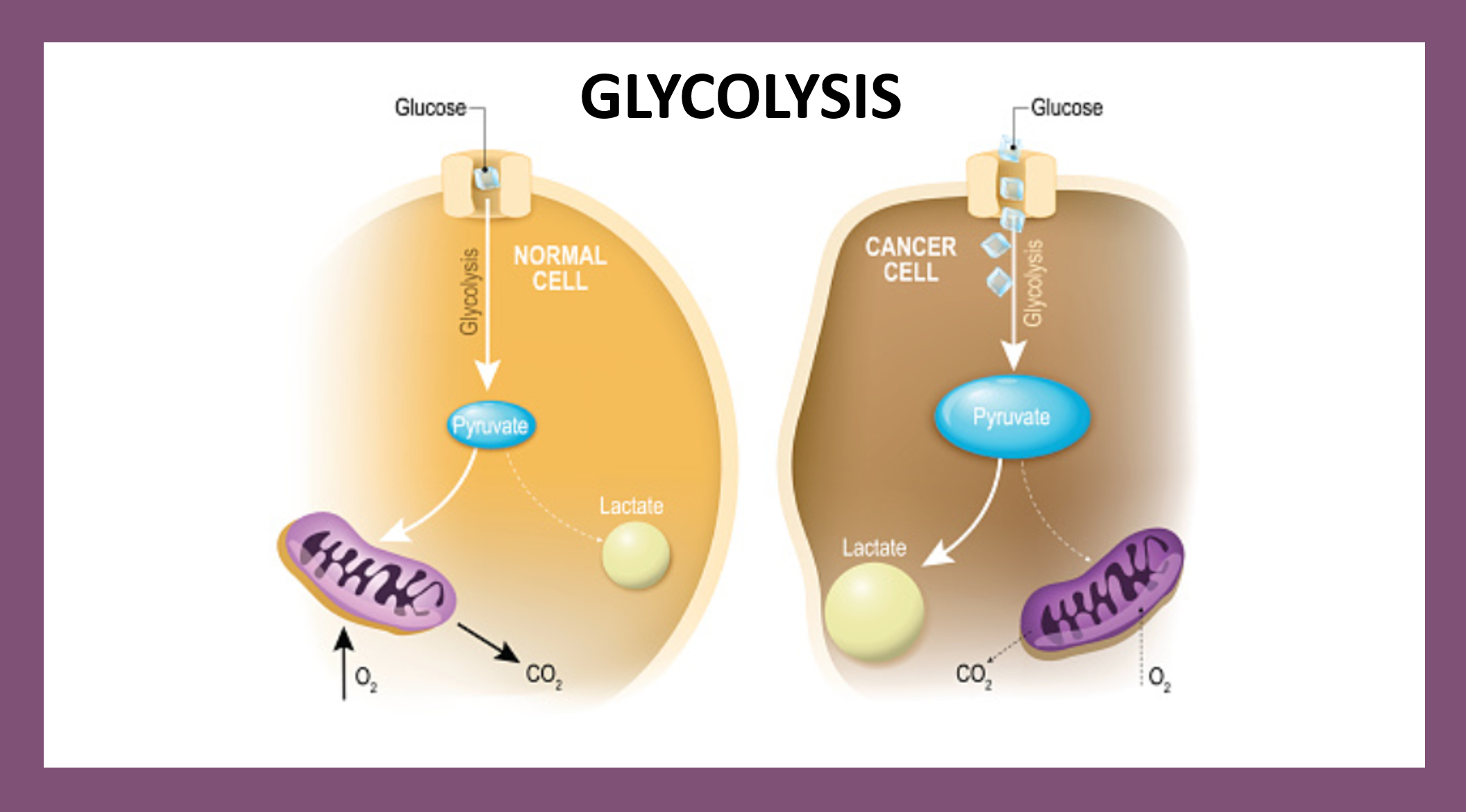
Glycolysis, one possible way to get energy
Glucose is the major energy source for mammalian cells as well as an important substrate for protein and lipid synthesis. It enters from extracellular fluid into the cell through two distinct families of structurally related glucose transporters. Once in the cells, glucose is transformed through


