
COSMETIC INDUSTRIES
We can help you confirming your claims
and compare product efficacy
Compare product efficacy
Dose effect analysis
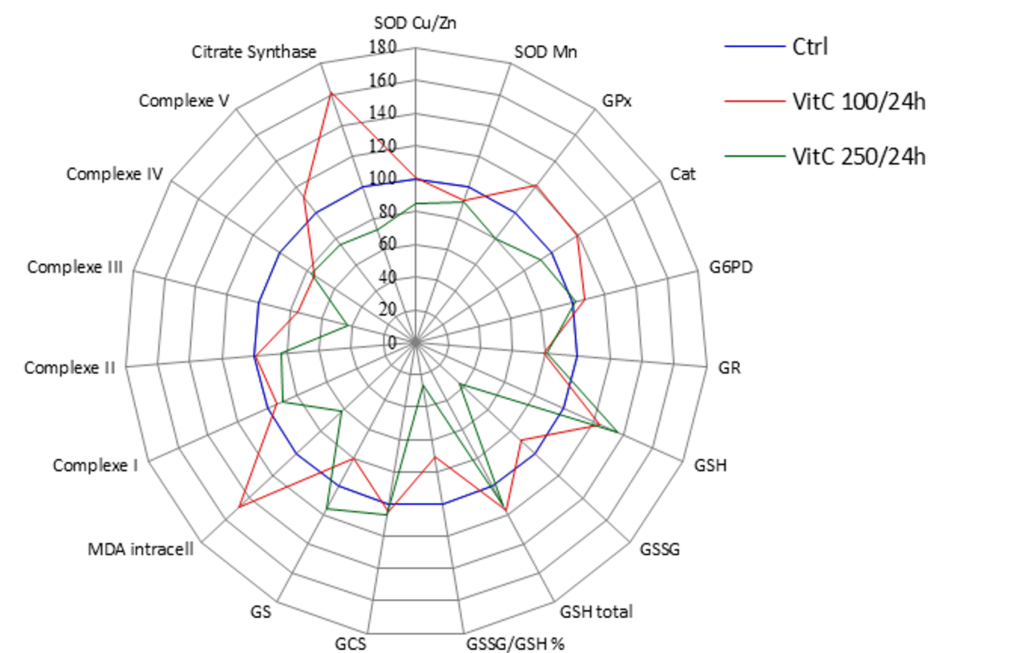
Comparison of two doses of Vitamine C on keratinocytes
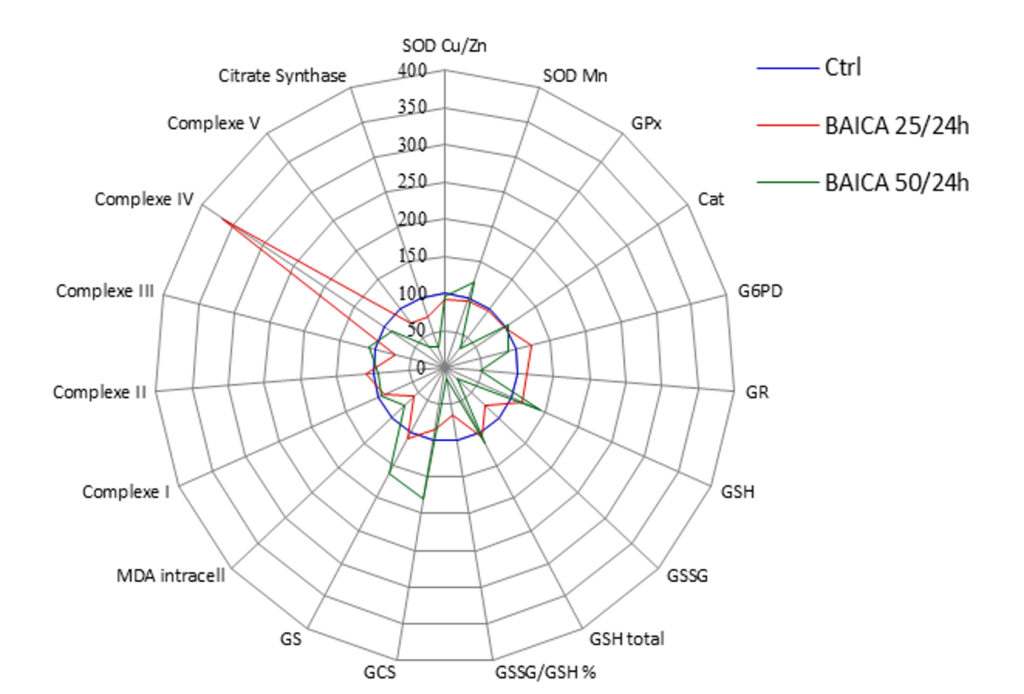
Comparison of two doses of Baicaline on keratinocytes
Time effect analysis
We can help you to find the optimal contact time of your ingredients with your model, in order to obtain the best effect.
Effect of unique dose of Baicaline during two different times on keratinocytes
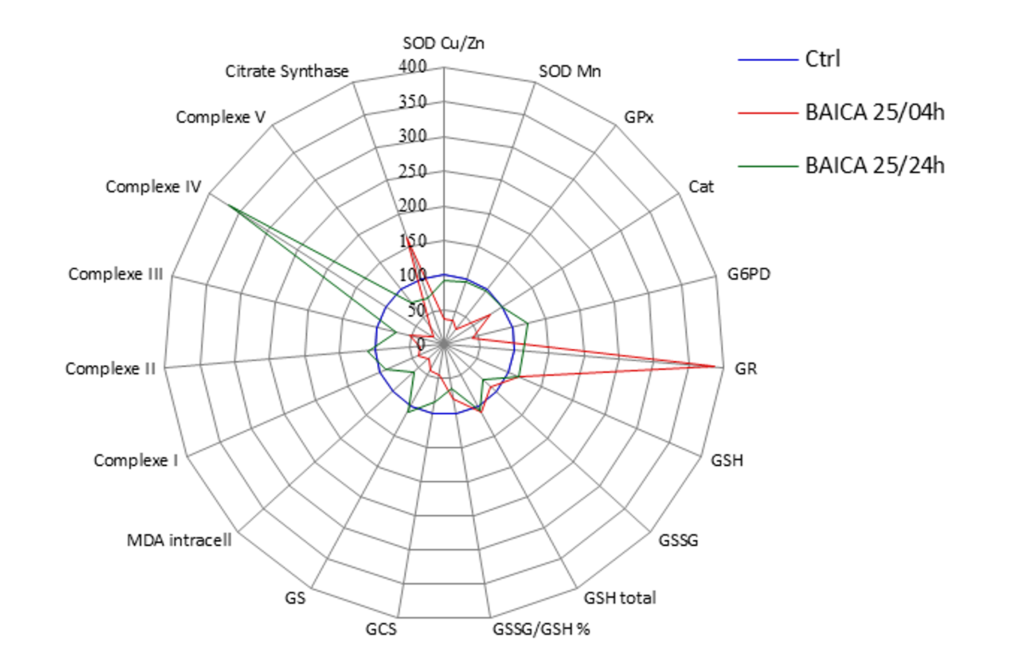
Product comparison
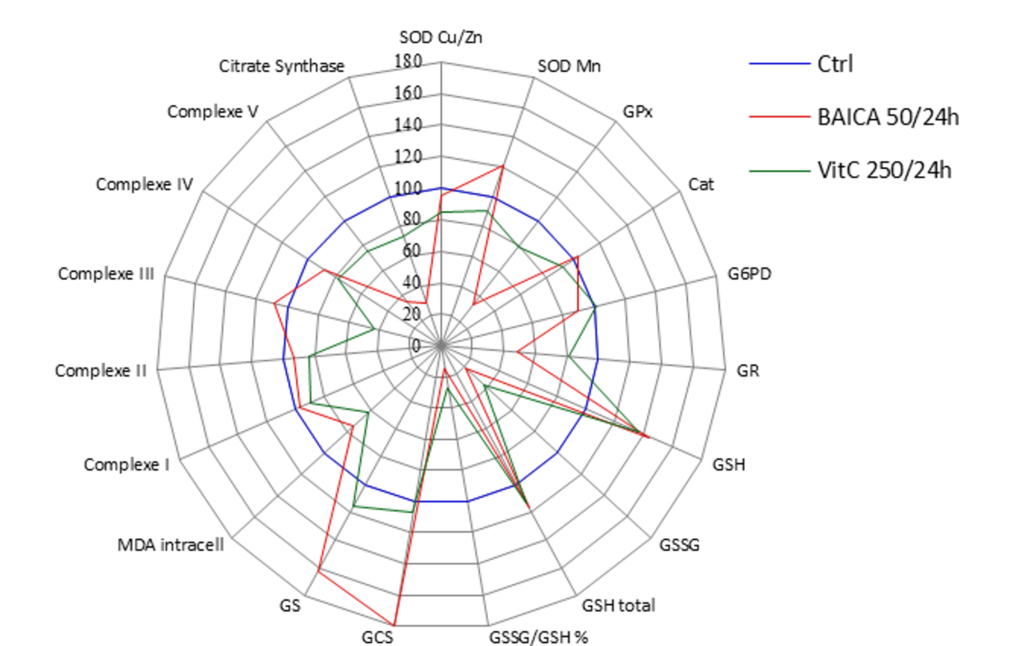
Comparison between Vitamine C and Baicaline effects on keratinocytes
Prove your claims
Antiaging
In our body, molecules oxidation, is today considered to be one of the major molecular mechanisms involved in the aging process. With age, accumulation of oxidative damage on human metabolism enzymes is responsible for a decrease in their efficiency. However, several enzymes act as the cellular tools that limit free radicals impact, by preventing radical hyperproduction or repairing free radicals damages. We must therefore ensure the integrity of our anti-oxidant system.
At the heart of our cells, mitochondria play a key role. They are essential to our body function. Any disturbances affecting them will play a central role in the aging process. Thus, preserving mitochondria therefore becomes essential. To evaluate this, we must control the reality of mitochondrial function. Any mitochondrial dysfunction will be a sign of cellular alteration.
Unfortunately, mitochondrial energy production, in the form of ATP, decreases in parallel with free radicals increase. These radicals end up damaging mitochondria themselves, either by degrading the enzymes that enable energy production or by altering mitochondrial DNA. Thus, over the years, mitochondria produce less and less energy and more and more radicals, which amplifies the phenomenon.
Collagen synthesis depends directly on fibroblasts that produce it, their vitality, their energy reserves, and finally their mitochondrial integrity. Moreover, collagen accelerated degradation is directly linked to radical production.
Any formulation that, after a specific stress, restores an altered antioxidant balance and preserves mitochondrial activity will limit aging alterations.

Pollution
Air quality (ozone, micro and nano particles,..), radiation (UV A, B, blue light, nuclear radiations,…), pollution (lead, mercury, aluminium, organochlorinated products…), treated water (denatured by chlorine and fluorine), industrial food (pesticides, herbicides, antibiotics, growth hormone, GMOs, cobalt 60 radiation, additives…), electromagnetic pollution (waves, low electromagnetic fields, various radiations….), stress (vulnerability to viruses, bacteria, toxins…) – the list is far not exhaustive – are all inducers of oxidative stress and mitochondria destroyers .

The link between pollution and oxidative stress is now well documented. This stress triggers a series of cellular events with multiple consequences : inflammatory response, cell proliferation modulation , and even cell death.
Oxidative stress thus is a major factor in the signalling cascades that lead to secretion of chemical mediators involved in these pathways. Depending on oxidative stress intensity, it can lead to progressive cellular responses or more or less significant lesions.
Low production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) induces activation of cellular antioxidant systems. If this protection is insufficient, oxidative stress increase generates a cascade of response including an inflammatory one. When all defenses are overwhelmed, it can lead to cell death.
This hierarchy of responses is directly related to the pro-oxidant/antioxidant balance, which itself varies largely from one individual to another.
Decreased expression or alteration of antioxidant enzymes can therefore increase sensitivity to pollutants and lead to a worsening, or even a triggering, of disorders. Similarly, the environment has a major impact on our mitochondria. Mitochondrial ATP production by oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) naturally generates free radicals, but when summed with environment derived free radicals, the balance becomes unbalanced, free radicals overproduction being even more aggressive on our mitochondria and reducing life expectancy.
Your preparation will display an anti-pollution effect if, after a specific stress, it is able to restore an altered antioxidant balance and help to preserve mitochondrial functionality.
Antioxidant
Oxidative mechanisms are normal and even for most vital ones as they are mandatory for proper cell functions. Every cell of our body is perfectly adapted. It has strong defense mechanisms that are largely scaled to fit the need of an efficient fight against ROS that these oxidative metabolisms generate.
A very large number of daily situations have a deleterious effect on these deep cellular mechanisms. These can be:
- exogenous stress : environmental (pollution, UV,…), medicinal, heavy metals, irradiation,…
- endogenous stress: nutritional deficiencies, genetic abnormalities, diseases, detoxification, intense metabolic activity (digestion, exercise, …)
Free radicals attack a lot of cells in the body, particularly they can damage nucleic acids, proteins, and lipids.

These free radicals can trigger very destructive oxidation chain reactions. The state of all oxidation reactions in the body is called the oxidative state. As all the above-mentioned factors can induce oxidative stress, it is usual that initially there is a passage through this state. After that, cellular rebalancing with antioxidant defense systems stimulation is generally observed. Thus, everything is therefore an issue of dynamic balance between radical attack and defense that thwart it.
If radical flow generated by the attack is too huge for defense level, and/or if defense level is weak for other reasons, then it can be hardly noticed that the oxidative state does persist then settles. At that time, one can then speak of oxidative stress.
An antioxidant product can act in several ways:
- a preventive way. Antioxidant treatment prior to the radical attack will allow the body to better resist. It is interesting to note that an antioxidant product does not necessarily increase cells « visible » defense level, but it would generally allow cells to resist the aggression longer and more effectively. It means that, in the absence of stress, no significant differences in defense levels will be observed in the treated group as compared to the untreated group. After an oxidative aggression, defense level of the treated group would be maintained at a higher level than those of the untreated group.
- a curative way. It renders possible to strengthen defenses that have been decreased by an oxidative aggression.
Since oxidative mechanisms have a major impact on mitochondria, it is mandatory to evaluate mitochondrial functionality and associate it with oxidative status evaluation.
Photosensitization, solar protection, blue light
The sun is essential to life on Earth. However, new habits like tanning at any cost (e.g. the rise of UV cabins) has been rapidly accompanied by an increase in skin cancer and accelerated skin aging.
Solar radiation is mainly composed of five different types of radiation: Infrared, Visible light, Ultraviolet, X-rays, Gamma rays, etc.
They differ from each other by their wavelengths and the amount of energy they carry. The more energetic the radiation is, the more harmful it is.
The most harmful radiations are gamma rays and X-rays, fortunately not all of them reach the skin as the ozone layer in the upper part of the atmosphere stops gamma rays, X-rays and the most energetic part of ultraviolet rays.

When they reach the skin, the radiation has variable effects:
- Infrared rays are not visible and bring a sensation of heat. Displaying low energy, their role in skin aging or in the occurrence of skin cancer is considered as minor.
- Visible light is composed of the colors of the rainbow spectrum. It is more energetic than infrared but its role is considered as minor in skin aging, but it may be involved in some solar allergies.
- Ultraviolet (UV) rays are the most energetic radiations, thus the most harmful. They can be divided into three types. UVA and UVB are able to damage skin while UVC, the most dangerous, stopped by the ozone layer, fortunately does not reach us.
+ UVA forms the bulk of UV radiation. Active throughout the day, they produce a quick but short-lived tan. UVA rays penetrate deep into the skin and can cause damage to the lower layers of the skin. These rays cause burns, wrinkles, skin spots, brown skin, precancerous skin lesions and skin cancers. UVA promote formation of very agressive free radicals that can break DNA. Their accumulation weakens skin’s defenses and reduces its immunity allowing undestroyed abnormal cells to multiply freely and lead to skin cancers.
+ UVB is a small fraction of UV radiation. They cause a slower but longer-lasting tan. Sun’s UVB rays damage the surface layer of the skin, causing burns and cancers. UVB can also break DNA and lower skin immunity.
Skin type is a key risk factor for skin cancer. Children’s skin is more sensitive to the sun’s rays than that of adults. It is important to notice that a sunbed emits at least 6 times more UVA rays than afternoon natural sunlight in a Mediterranean country.
Aside photosensitization, photosensitivity, sometimes called « sun allergy », that may occur during sun exposition, is an immune system reaction triggered by sunlight.
The blue light emitted by our TV screens, our tablets, our smartphones, our LED lamps… is sneaky. While we feel the effects of UVA, UVB that burn and those of infrared rays that heat our skin, blue light is perfectly painless. Blue light induces skin oxidation. It releases free radicals, causing cell membranes oxidation and thus altering regeneration system of skin cells. As a result, complexion becomes duller, less homogeneous and imperfections appear. Consequences are not immediately visible but premature skin aging does exist. Along with sun and pollution, exposure to blue light is considered as the third factor responsible for premature skin aging. .
Your preparation will have an antiradiation effect if, after a specific stress, it restores an altered antioxidant balance and if it helps to preserve mitochondrial functionality.
